
Phospholipids
Krill oil contains specialized fat molecules called phospholipids
The omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA are bound to these phospholipids. The phospholipid-bound forms of omega-3 fatty acids seem to have select advantages in how they are absorbed and utilized by the human body. A small number of studies have examined how phospholipid-bound fatty acids are used in comparison to triglyceride forms.
Phosfolipids are the building blocks of cell membranes and present the best source of omega-3 and omega 6 fatty acids. Krill omega-3s are transported and integrated into cell membranes quicker and more efficiently because they are bound to phospholipids.

Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient found in krill oil, similar to the B vitamins
Choline is a biochemical building block imprtant for liver, heart and congitive health
It is used in the structure of cell membranes, protects the liver from accumulating fats, and is important to the transmission of nerve impulses (neurotransmission) in brain.
Choline supplementation is especially important for vegetarians, vegans and people who over-consume alcohol, since these groups are known to have an elevated risk of choline deficiency.

Astaxanthin
Antioxidants enter your blood and scavenge for DNA-damaging free radicals. Free radicals are formed when a molecule in your cells loses an electron. This can be triggered by the presence of environmental factors such as pollution, radiation, herbicides or smoking (among many other agents). Free-radical activity can even be triggered by consumption of excessive calories, such as those found in simple sugars.
Free radicals are unstable and they try to steal their needed electron from another compound – a method used to gain stability.
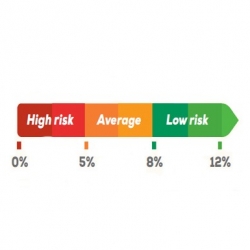
Omega 3 index
The Omega-3 Index offers a window into a person’s general state of health. It is a reliable diagnostic tool that presents the combined EPA and DHA concentration as a percentage of total fatty acids in blood. By recording the percentage concentration of omega-3s in red blood cells, the Omega-3 Index provides a useful indication of a person’s long-term intake of these fatty acids.
Because the Omega-3 Index reflects the incorporation of omega-3s in cell membranes, which provide numerous health benefits, the Omega-3 Index is suggested to correlate with both the health of the body and its omega-3 status.
